is Operator
Syntax: variable1 is variable2
a = [1, 2, 3] b = [1, 2, 3] result = a is b # False
is not Operator
Syntax: variable1 is not variable2
a = [1, 2, 3] b = [1, 2, 3] result = a is not b # True
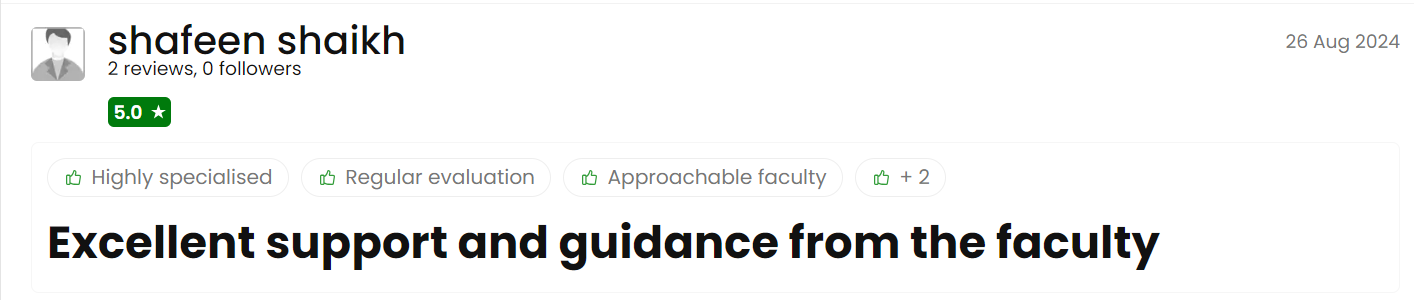
Python program that demonstrates the use of Identity operators:
# Identity Operators in Python
# Defining two variables
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = [1, 2, 3]
# Comparing memory locations of the variables
print("a is b:", a is b) # False, because 'a' and 'b' are different objects with the same content
print("a is not b:", a is not b) # True
# Using identity operators with the same object
c = a
print("a is c:", a is c) # True, because 'a' and 'c' refer to the same object
print("a is not c:", a is not c) # False
# Using identity operators with a singleton
x = None
y = None
print("x is y:", x is y) # True, because None is a singleton object
print("x is not y:", x is not y) # False
Output
a is b: False a is not b: True a is c: True a is not c: False x is y: True x is not y: False